New energy vehicle insurance refers to the risk protection for new energy vehicles, mainly including vehicle loss insurance, third-party liability insurance, onboard personnel liability insurance, etc. Compared with traditional fuel vehicle insurance, new energy vehicle insurance has certain differences in coverage, rates, and other aspects. According to the "New Energy Vehicle Insurance Market Analysis Report" released by China Banking and Insurance Corporation (CBIT), the average premium of new energy vehicles is actually about 21% higher than that of gasoline vehicles. This difference is mainly attributed to the following aspects:
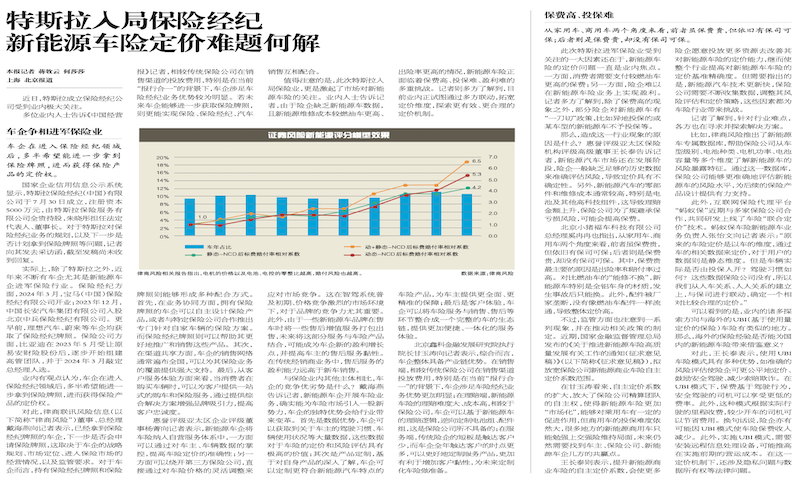
Accident rate: The accident rate of new energy vehicles is generally higher than that of traditional fuel vehicles. The report points out that the accident rate of household new energy vehicles is as high as 30%, significantly higher than the accident rate of 19% for gasoline vehicles. New energy vehicles have become the preferred choice for many novice drivers, and the preferential registration policies enjoyed in certain regions may lead to an increase in the accident rate of new energy vehicles.
Maintenance cost: According to a statistical analysis conducted by We Predict, an American data analysis company, the maintenance cost of electric vehicles is 1.6 to 2.3 times that of internal combustion engine vehicles. On the one hand, this is due to the significantly longer maintenance time of electric vehicles compared to traditional fuel vehicles, and on the other hand, it is due to the extremely high replacement prices of electric vehicle parts. Unlike traditional fuel vehicles, electric vehicles can be repaired on a small scale to address the areas of wear and tear. Due to manufacturing and design issues, even minimal wear and tear may result in the replacement of the entire battery pack, and the repair price may even exceed the price of a new vehicle. The significant increase in overall maintenance costs has led to high claims from new energy vehicle owners after accidents, resulting in a high payout situation for new energy vehicle insurance.
Compensation amount: The average compensation for new energy vehicles is generally higher than that for traditional fuel vehicles. According to statistics, among the household vehicles with the highest proportion of usage, the compensation rate for new energy vehicles is about 30 percentage points higher than that for fuel vehicles, with a compensation amount of 7201 yuan, nearly 600 yuan higher than that for fuel vehicles; In non commercial trucks, the difference in compensation rate between new energy vehicles and fuel vehicles is about 7%. In terms of third-party insurance, the payout rates for new energy vehicles are higher than those for traditional fuel vehicles, with payout rates exceeding 100% for household vehicles, non commercial buses, and non commercial trucks.
Depreciation rate: The rapid technological updates of new energy vehicles may lead to higher depreciation rates. A high depreciation rate may mean a greater loss of vehicle value in accidents, thereby increasing the potential payout risk for insurance companies.
The basis for formulating insurance premiums for new energy vehicles
Factors to consider for the premium of new energy vehicle damage insurance:
Vehicle loss insurance is a risk protection for new energy vehicles themselves, and the premium calculation mainly considers the following factors:
Car price: New energy vehicles, especially those equipped with advanced batteries and technology, often have higher purchase prices. This directly affects the calculation of the premium base, as higher purchase costs mean higher compensation amounts in the event of vehicle damage. Compared to traditional fuel vehicles, the premium of new energy vehicles may be higher as a result.
Vehicle age: For new energy vehicles, vehicle age not only reflects the vehicle's usage time, but may also affect battery performance and overall vehicle maintenance status. The degradation of battery performance over time may increase the cost of future maintenance or replacement, which requires special consideration when assessing insurance risks.
Vehicle types: There are various types of new energy vehicles, including pure electric vehicles, plug-in hybrid vehicles, etc. The differences in technology and construction of different vehicle models result in different risk assessments. For example, pure electric vehicles may face higher risks of spontaneous combustion due to the large capacity and high energy density of the battery pack, which needs to be reflected in the premium calculation.
Specific risks: New energy vehicles may face specific risks, such as battery self ignition, electrical system water damage, etc., which are relatively rare or manifest differently in traditional vehicles. The special characteristics of batteries and electrical systems in new energy vehicles require insurance companies to conduct more detailed risk assessments and may charge additional premiums for these specific risks.
Factors to consider for third-party insurance premiums for new energy vehicles:
Third party liability insurance is a risk protection for third-party damage caused by new energy vehicles, and the premium calculation mainly considers the following factors:
Compensation limit: The policyholder selects the compensation limit based on their own needs, which directly affects the level of insurance premiums. For new energy vehicles, policyholders may prefer to choose higher compensation limits to obtain more comprehensive risk protection due to their high repair costs or special damage compensation needs (such as chain reactions caused by battery leaks or electrical system damage).
Vehicle age: The age of new energy vehicles also affects the calculation of third-party liability insurance premiums. As the service life increases, on the one hand, the maintenance and battery performance of the vehicle may decrease, which may indirectly affect driving safety.
Accident records: The historical accident records of new energy vehicles are an important factor in evaluating their risks and adjusting premiums accordingly. Due to the different driving and operational characteristics of new energy vehicles (such as the instantaneous acceleration ability of electric vehicles), these characteristics may affect the incidence and types of accidents. Therefore, when considering the accident records of new energy vehicles, insurance companies will pay special attention to the unique risk patterns that these vehicles may present.
Factors to consider for seat insurance premiums for new energy vehicles:
Vehicle personnel liability insurance is a risk protection for new energy vehicle occupants, and the premium calculation mainly considers the following factors:
Number of passengers: The calculation of premium is first based on the number of passengers on the vehicle, which may be different from traditional fuel vehicles for new energy vehicles. The design of new energy vehicles may place greater emphasis on space utilization and ride comfort, thereby affecting the setting of the number of passengers. Some new energy vehicle models may provide more spacious interior space (such as Tesla Model Y), allowing more passengers to ride safely, which directly affects the number of policyholders and corresponding premium calculations.
Risk level: The risk level assessment of new energy vehicles integrates their unique driving characteristics, highly electrified operating systems, maintenance and technological update needs, as well as the driver's adaptability to these new technologies. These vehicles typically provide smooth and fast acceleration performance, as well as intelligent driving assistance functions, aimed at improving safety and driving convenience. These characteristics require drivers to have the corresponding knowledge and experience to fully utilize these advanced features and maintain safe driving. In addition, new energy vehicles may require more frequent software updates and electronic system maintenance to maintain optimal performance and safety standards. Therefore, the service life of vehicles, the adaptability and experience of drivers, and the frequency of vehicle maintenance and updates collectively affect the risk level of new energy vehicles, which requires insurance companies to comprehensively consider when evaluating premiums.
Specific risk: same vehicle damage insurance.
The mechanism that leads to high premiums
Short term mechanism: The market's understanding of new energy vehicles is still insufficient, which affects consumers' willingness to purchase new energy vehicle insurance and insurance companies' accurate assessment of risks. Due to the relatively new nature of new energy vehicles, the insurance industry lacks sufficient historical data to accurately assess the associated risks, which increases the uncertainty and risk premium for insurance companies in pricing. According to incomplete statistics from Cyber Automotive, a total of 70 new energy vehicles were launched in 2022 (excluding models with facelifts, upgrades, and updated versions). Among them, there are 56 pure electric vehicle models, 5 plug-in hybrid models, 4 extended range models, and 5 pure electric and plug-in hybrid models.
At the same time, the integration level of the new energy vehicle insurance industry chain is not high, especially the synergistic effect between upstream and downstream has not yet been fully formed. Insurance companies, car companies, and big data monitoring platforms have not yet reached comprehensive cooperation: insurance companies with insurance qualifications and operational capabilities do not have sufficient data, while car companies with sufficient data and big data monitoring platforms do not have insurance qualifications and operational capabilities, and the three parties are deeply trapped in the data wall. Although top insurance companies are able to seize opportunities in this emerging market due to their financial strength and data processing capabilities, small and medium-sized insurance companies face greater challenges. According to data from the China Insurance Industry Association, since 2011, the market concentration (CR3) of the car insurance industry has been maintained in the range of 65% -70%, with market share mainly concentrated in top property and casualty insurance companies such as PICC, Ping An Property and Casualty Insurance, and Taiping Property and Casualty Insurance. For small and medium-sized insurance companies, they face a dilemma: on the one hand, they cannot ignore the huge potential market for new energy vehicle insurance, and opportunities for lane changing and overtaking are within reach; On the other hand, it is also difficult to avoid the current situation of high insurance coverage and compensation for new energy vehicles. Compared to leading enterprises, their risk pricing, product innovation, and service capabilities do not have an advantage, and they will face significant underwriting loss pressure. At the same time, new energy vehicle companies are also eyeing the automotive insurance industry, with sufficient internal data and a better understanding of automotive risks, which is no different from another huge pressure on small and medium-sized insurance companies.
In addition, the proportion of new energy exclusive car insurance in the entire insurance market is relatively small, which limits the ability of insurance companies in data statistics and analysis. Without sufficient case studies and data support, insurance companies find it difficult to build accurate risk assessment models, which may lead to a more conservative attitude in pricing strategies to cover potential unknown risks, thereby driving up premiums for new energy vehicle insurance.
Medium - and long-term mechanism: The continuous progress of new energy vehicle technology not only promotes the improvement of vehicle performance, but also brings uncertainty in maintenance and component replacement costs. With the development of technology, some initial high cost issues may be solved, such as the cost of batteries and electric drive systems may decrease as technology matures. However, at the same time, the introduction of new technologies and materials may also bring new cost challenges.
The development of the new energy vehicle insurance market is not only related to risk management, but also to the construction of new business models. From the perspective of insurance company operations, the cooperation model between new energy vehicles and automobile manufacturers has to some extent overturned the traditional operation mode of insurance companies in the automotive insurance business. This requires insurance companies not only to adjust their product structure to meet the specific needs of new energy vehicles, but also to restructure their organizational structure in order to more effectively respond to changes in the market and sales channels.
In the medium to long term, insurance companies need to explore deeper cooperation opportunities with new energy vehicle manufacturers, technology providers, and service networks to build more flexible and efficient operating models. This includes developing more personalized insurance products, utilizing big data and artificial intelligence technology to optimize risk assessment and pricing strategies, and enhancing customer service experience through digital platforms and tools.
impact analysis
Reduced market acceptance: High premiums may significantly reduce consumers' willingness to purchase new energy vehicles, thereby affecting the market penetration rate of new energy vehicles. Especially for first-time car buyers or consumers considering cost-effectiveness, high premiums have become the main driving force for choosing traditional fuel vehicles over new energy vehicles.
Increased operating costs: For enterprises that rely on new energy vehicles for commercial operations (such as taxis, shared car services, etc.), high premiums directly increase their operating costs. This may lead to an increase in service prices, thereby affecting consumer willingness to use and overall market demand.
Damage to consumer confidence: High premiums for new energy vehicles may lead to misunderstandings or excessive concerns among consumers about the maintenance, repair costs, and accident risks of new energy vehicles, thereby affecting their confidence in purchasing new energy vehicles.
Suggestions for countermeasures
Accelerate the integration of insurance technology: Moving towards customized car insurance: To address the issue of high premiums for new energy vehicles, the insurance industry needs to accelerate its integration with technology, especially in the areas of intelligent driving and vehicle networking technology. By utilizing the rich sensor data of new energy vehicles, insurance companies can develop personalized insurance products (UBI) based on user driving behavior. This approach not only provides more accurate risk assessment, but also promotes the personalization and intelligence of insurance products, thereby achieving more reasonable premium pricing and reducing consumer burden.
Strengthening the accuracy of risk pricing: relying on data-driven transformation: Insurance companies should further enhance the accuracy of their risk pricing, especially by deepening their analysis capabilities of comprehensive data on "people, vehicles, and environment". This requires insurance companies not only to strengthen their professional capabilities in risk management and data analysis, but also to work closely with car manufacturers to share vehicle and usage data. Through such cross-border cooperation, it can promote the transformation from sales driven to data-driven business models, and achieve more accurate and fair premium formulation.
Ecological insurance services: Deepening the automotive industry chain: The future development of new energy vehicle insurance should be more deeply integrated into the automotive industry ecosystem, becoming an important link in this ecosystem. This means that insurance products and services are not limited to traditional risk coverage, but should be closely integrated with post market services such as sales, maintenance, and repair of new energy vehicles, providing consumers with a one-stop, seamless service experience. Through this approach, insurance companies can better understand consumer needs and also provide value-added services to automobile manufacturers, jointly tapping into the potential of the new energy vehicle aftermarket.
Cross border cooperation and data sharing: Promoting coordinated development of industries: Faced with the challenge of high premiums for new energy vehicles, cross-border cooperation and data sharing between insurance companies, automobile manufacturers, and technology platforms are particularly crucial. By establishing a more open data exchange and sharing mechanism, all parties can collect and analyze real-time and accurate data on the use, maintenance, and driving behavior of new energy vehicles. This not only helps insurance companies develop insurance products that better meet market demand, but also helps automobile manufacturers optimize product design, ultimately achieving overall optimization of the new energy vehicle industry chain, reducing costs, and improving efficiency.
 Tesla enters the insurance brokerage and how to solve the problem of new energy vehicle insurance pricing
Tesla enters the insurance brokerage and how to solve the problem of new energy vehicle insurance pricing