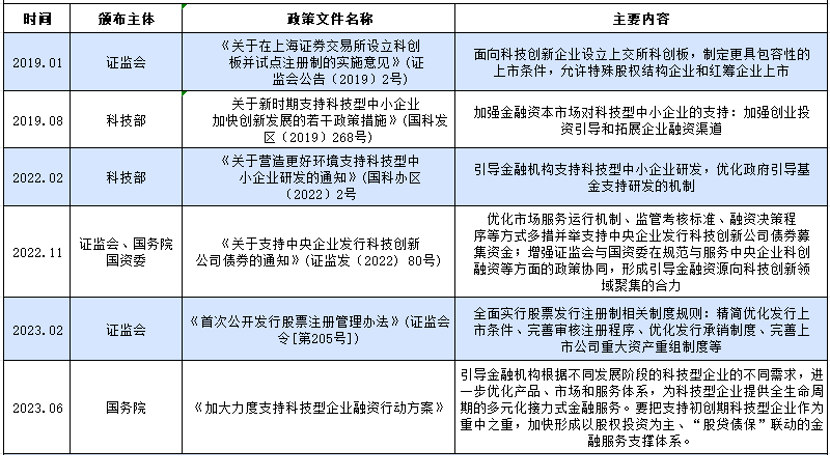
Against the backdrop of increasingly fierce global competition in technological innovation, the Chinese government attaches great importance to technological innovation. The report of the 20th National Congress of the Communist Party of China emphasizes the improvement of the technological innovation system to ensure its core position in modernization construction. Science and technology innovation enterprises are a key driving force for innovation, but their development cannot be separated from the support of the financial system. Building a financial system that supports science and technology innovation enterprises is crucial for enhancing national competitiveness and high-quality economic development. At present, Bank of China loans are the main source of financing for science and technology innovation enterprises, accounting for about 60%.
The government has launched policies to improve the financing system, including the establishment of the Science and Technology Innovation Board and a comprehensive registration system, aiming to provide more convenient financing channels for technology enterprises. However, the Chinese banking industry still faces challenges in supporting technology credit, such as the mismatch between banks' low-risk preferences and the high-risk characteristics of science and technology innovation enterprises, as well as structural imbalances in financing. This study will explore how the Chinese banking industry can improve its financial support system to better promote the growth and innovation of science and technology innovation enterprises.vv
Characteristics of the manufacturing-centric model
China is a manufacturing powerhouse with a high contribution rate to GDP, reaching over 30% since the end of 2015. Against the backdrop of increasingly fierce global economic competition, the development of high-end manufacturing has become an important means of achieving economic transformation and upgrading, and improving international competitiveness. However, currently, developed countries such as the United States, Germany, and Japan have prominent advantages in the high-end manufacturing industry, while China's development in the high-end manufacturing industry still has a long way to go.
In terms of the proportion of high-tech industries to the added value of manufacturing, Germany, Japan, and the United States all lead China. Among them, Germany's high-tech industries account for nearly 60% of the added value of manufacturing, while China's high-tech industries only maintain a proportion of about 40%. At the same time, the United States continues to impose technological blockades and trade restrictions on China, which poses greater challenges to the development of China's high-end manufacturing industry. Therefore, it is imperative for China to independently develop its high-end manufacturing industry.
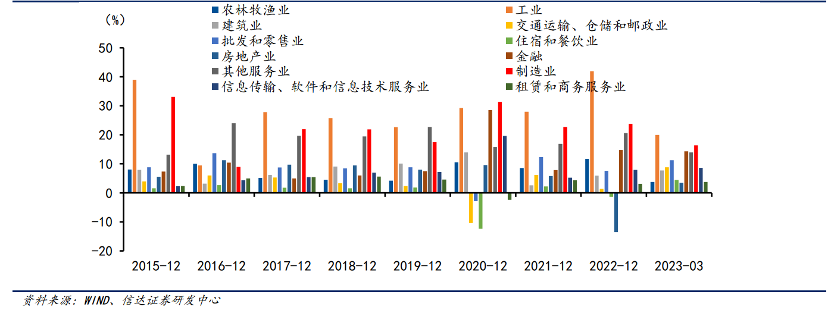
This model of China's manufacturing industry shows its firm position in the global manufacturing competition, and also highlights the need for sustained growth and innovation in high-end manufacturing.v
Traditional banking business model
Asset based business
The asset business of a bank involves various activities carried out using its own assets. In addition to providing short-term and medium to long-term loans, this also includes issuing personal housing loans, corporate loans, credit card loans, and other credit products. Banks charge interest through these loans as one of their main sources of income. Banks also participate in investment activities, such as purchasing government bonds and corporate bonds, as well as other market investments to increase asset returns.
Debt related business
Debt related businesses are based on bank lending activities, including deposit business and other forms of fund borrowing. Deposit business, including demand deposits and fixed deposits, is the core of bank liability business and provides a large source of funds for banks. At the same time, banks also raise funds from other financial institutions or markets through interbank lending, bond issuance, and other means, which are important components of their liability business. Among them, bank deposits are an important component of bank liability business, generally accounting for more than 70% of its total liabilities, and are the foundation for the survival and development of banks.v
Intermediate business
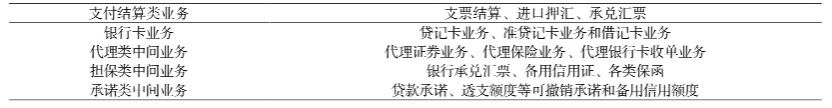
Intermediary businesses leverage the brand and professional advantages of banks to provide customers with indirect financing services, such as investment advisory, financial planning, asset management, and custody services. These services usually do not involve direct investment of the bank's own capital, but rather generate revenue for the bank through service fees, transaction commissions, and other means. Banks also provide various payment and settlement services, letter of credit opening, remittance, etc. These services help banks expand their market influence and enhance customer stickiness.
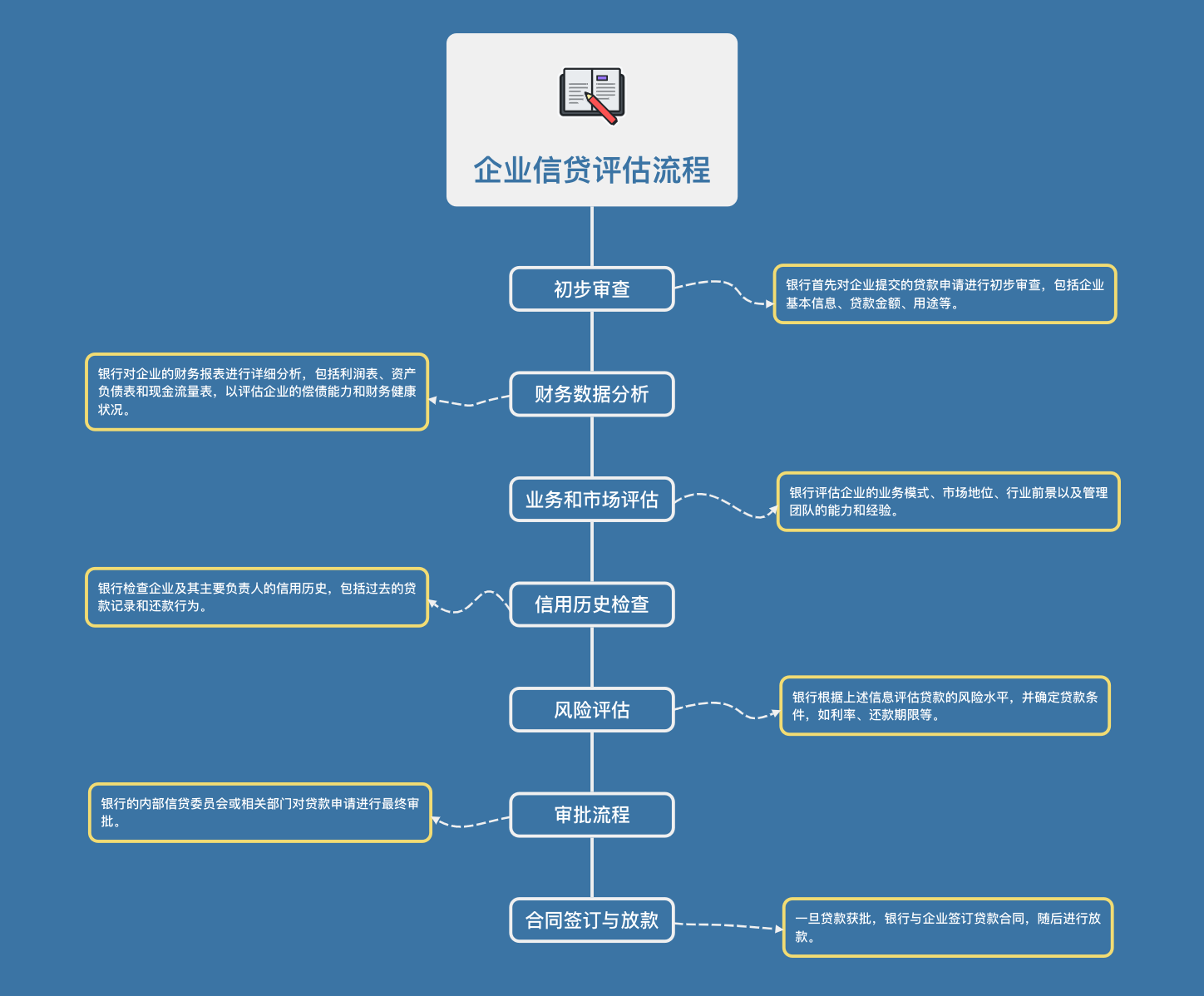
Credit Business Appraisal Process
Risk assessment elements
Financial condition analysis: Banks will focus on analyzing the financial reports of enterprises, including balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow statements. This can help banks understand a company's debt paying ability, asset quality, profitability, and financial health. Banks pay special attention to key financial indicators such as debt ratio, current ratio, and quick ratio.
Credit history review: The historical credit record of a company is the key to measuring its credit risk. The bank will check the credit score of the enterprise, past borrowing and lending records, repayment behavior, and whether there is a history of default or default. A good credit record can significantly increase the likelihood of loan approval.
Business Model and Market Competitiveness: Banks evaluate whether a company's business model is sustainable and its competitiveness in its market. This includes analyzing the customer base of the enterprise, supply chain stability, market demand for products or services, and the situation of competitors.
Management team evaluation: The management team of a company is crucial to its success. The bank will assess the experience, qualifications, performance records, and stability of the management team members. An experienced and efficient management team can effectively reduce the credit risk of a bank.
Economic and political environment: Banks will also consider the impact of macroeconomic and political environment on enterprises. Economic recession, political instability, or policy changes can all affect a company's profitability and debt repayment ability.
The value of collateral and guarantees: As part of risk control, banks will evaluate the value of collateral and guarantees provided by enterprises. These collateral may include real estate, equipment, or other valuable assets. The higher the value of the collateral, the more likely the bank is to consider the loan risk to be lower.
Limitations of the current banking model
Insufficient development of equity financing: Technology enterprises face significant risks during the pilot incubation stage, resulting in lower willingness of traditional financial institutions such as banks to participate. This situation exacerbates the structural contradiction between the low-risk preference of banks and the high-risk characteristics of science and technology startups, especially for startups with inadequate financial systems. In addition, imperfect risk compensation mechanisms, insufficient investment loan linkage, and a lack of innovative financial products make it difficult for banks to effectively integrate funds to support science and technology innovation enterprises.
Insufficient financial intermediary services: In the field of providing loan services for science and technology innovation enterprises, there is a lack of financial intermediary institutions that can effectively connect enterprises, governments, investment platforms, and banks. This lack leads to poor information flow, making it difficult for enterprises to obtain necessary financial services and support. Due to the lack of professional financial intermediary services, the problem of information asymmetry between banks and science and technology innovation enterprises has become more prominent, which further exacerbates the conservative attitude of banks towards loan approval for science and technology innovation enterprises, thereby affecting the financing efficiency and cost of science and technology innovation enterprises.
Intellectual property evaluation and guarantee issues: When evaluating the value of intellectual property, banks overly rely on third-party institutions, and there is a lack of unified and authoritative evaluation standards in the market. This leads to inconsistency and uncertainty in the evaluation results. Meanwhile, due to the professionalism and complexity of intellectual property, banks usually hold a cautious attitude when providing guaranteed loans. This caution may hinder the acceptance of intellectual property as collateral by banks, especially when it comes to intangible assets of start-ups.
Limitations of credit evaluation system: The current credit evaluation system mainly focuses on enterprises with a history of loans, and there are evaluation blind spots for high-quality enterprises that have not yet been exposed to loans. The existing evaluation system overly relies on the financial statements of enterprises, neglecting the important aspects of evaluating the credit of the management team and the market potential of the enterprise. This single dimensional evaluation method is not conducive to a comprehensive understanding of the real business situation of science and technology innovation enterprises, and may also lead to banks missing opportunities to support innovative enterprises with high growth potential.
Authors: Gan Yutao, Chu Xianghe, Yu Yue